

Order to calculate the combined effect of thermal and dynamic loading. Theĭynamic model can likewise be coupled to the optional thermal model in Time-dependent pore pressure change associated with liquefaction.
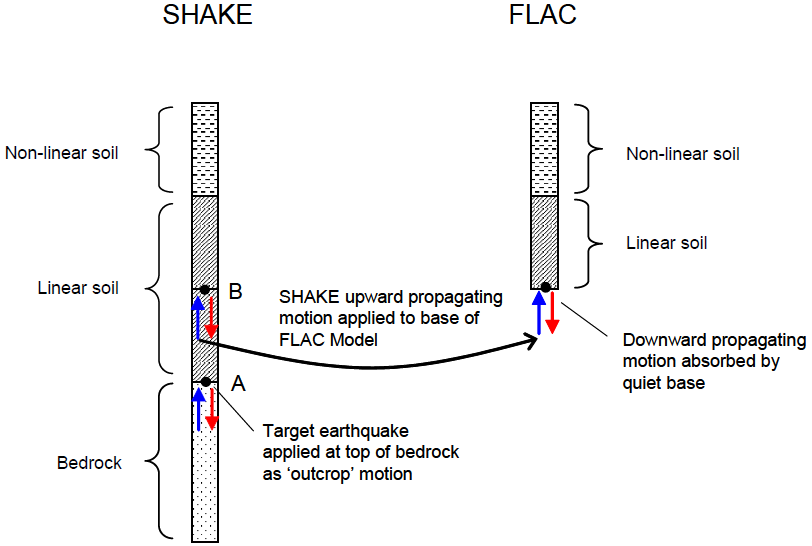
This allows, for example, analyses involving The dynamic feature can also be coupled to the Permitting analysis of soil-structure interaction brought about by This option can be coupled to the structural element model, thus FLAC3D contains absorbing andįree-field boundary conditions to simulate the effect of an infinite User-specified acceleration, velocity, or stress waves can be inputĭirectly to the model either as an exterior boundary condition or an Permits three-dimensional, fully dynamic analysis with FLAC3D. IMASS is available as a built-in, optional constitutive model for FLAC3D(version 7.0 or later) and is sold as a separate, monthly or annual lease, license. This two-stage softening/weakening behavior in IMASS is critical to accurately represent the rock mass post-peak behavior for underground and surface mining applications. IMASS uniquely contains two softening (or residual) yield envelopes to represent the two-stage softening behavior for a rock mass that distinguishes between damage (caused by fracturing and the associated loss of cohesion and tensile strength) and the subsequent disturbance (due to bulking) in rock mass behavior.
IMASS is based on empirical relationships and uses strain and zone-size dependent properties that reflect the impacts of dilation and bulking as a rock mass undergoes plastic deformation. IMASS represents the damage around an excavation, slope, or caving process by accounting for the progressive failure and disintegration of the rock mass from intact, jointed, and/or veined rock to a disaggregated, bulked material. The Itasca Constitutive Model for Advanced Strain Softening ( IMASS) has been developed to represent the rock mass response to excavation induced stress changes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
